
In top form
More power, more torque, more efficiency: The new turbocharged engines in the 911
The end of one game is the beginning of the next. The 911 development team has taken this old German saying from the world of sports to heart. Immediately after the current generation of the
Elite athletes define themselves by impressive numbers. Take the 272 kW (370 hp) 911
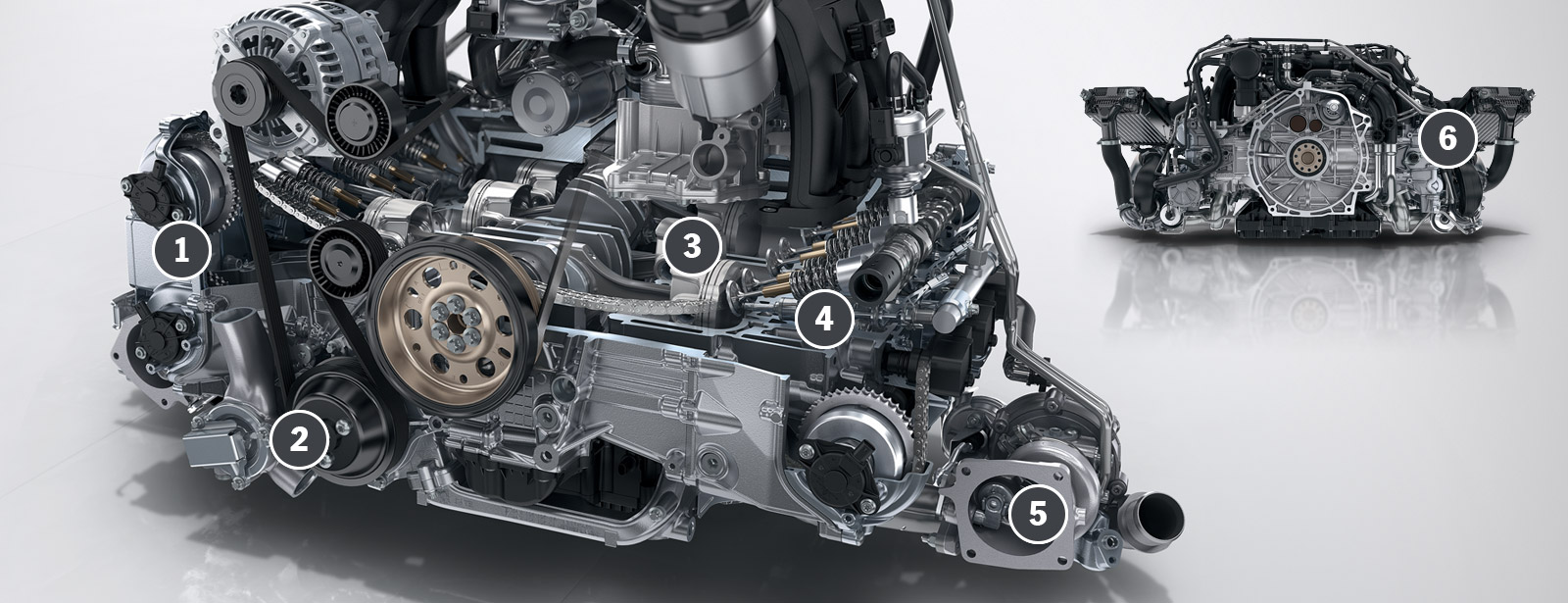
1 VarioCam Plus
In the new boxer engines, the valve timing for the camshafts is variable on the intake and exhaust sides. The lift for the intake valves can be varied as well.
2 Water pump
A dynamic water pump helps the engine reach its operating temperature more quickly after the start.
3 Crankcase
An iron-based coating of the cylinder liners ensures extremely low friction and low oil consumption.
4 Direct fuel injection
The fuel injectors are positioned centrally and inject the fuel at pressures of up to 250 bar.
5
Two turbochargers ensure consistently high torque between 1,700 and 5,000 rpm.
6 Charge-air cooling
The compressed air behind the turbocharger is cooled with ambient air to improve performance.
“How are these significant performance and efficiency gains achieved?” To answer the question, Thomas Krickelberg picks up a piece of paper that explains it all. He’s in charge of project management for the 911 power trains. The sheet shows the torque curve of the new three-liter boxer engine generation being used in the 911
Achieving that goal was a major priority for the engineers. The objective: minimizing turbo lag. A whole series of measures was implemented to make it happen. For instance,
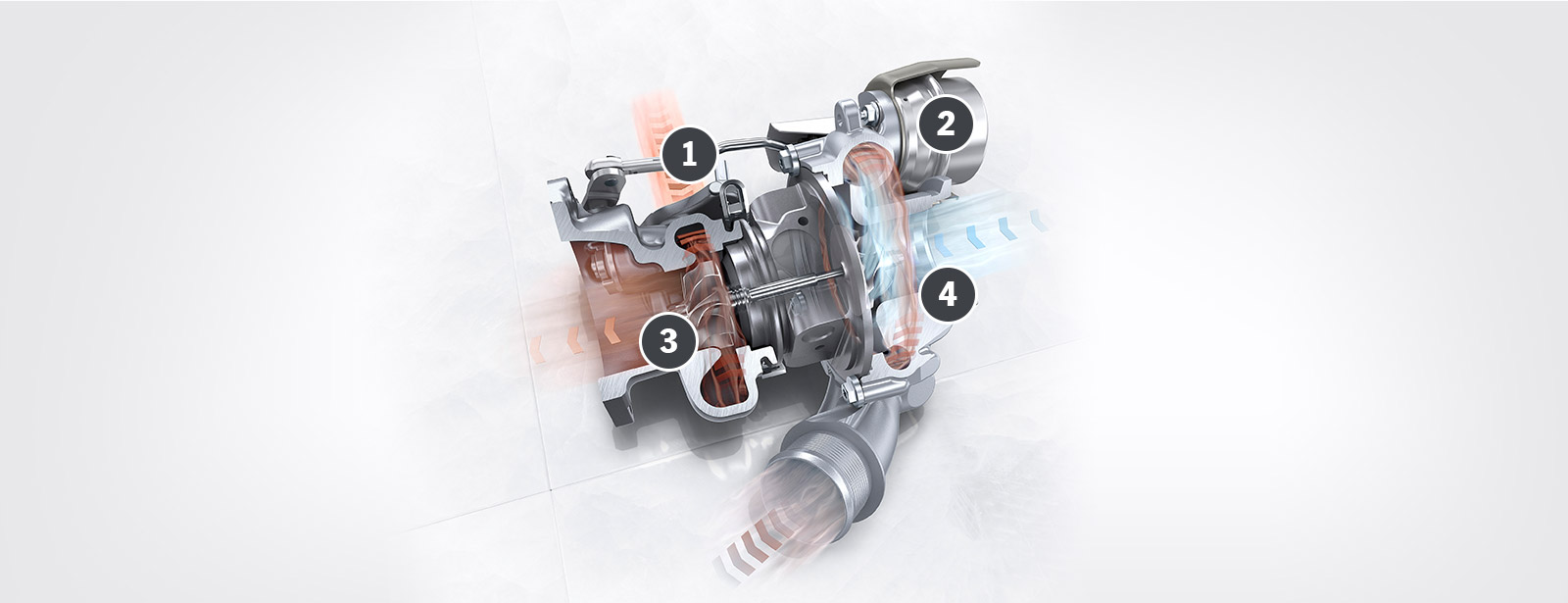
1 Arrangement
Because the two turbo-chargers are positioned near the cylinder heads, very little exhaust energy is lost and throttle response is improved.
2 Wastegate
An electro-pneumatic wastegate actuator ensures rapid regulation of the exhaust flow.
3 Turbine wheel
The turbine wheel is driven by the exhaust flow and transmits the kinetic energy to the compressor wheel positioned on the same shaft.
4 Compressor wheel
The compressor wheel ensures that the intake air reaches the combustion chamber with overpressure.
For the overall performance of a turbo engine, cooling the charge air is crucial: when compressed, the intake air temperature rises, which results in unfavorable air expansion, reducing the number of oxygen molecules that are required for combustion to reach the combustion chamber. On account of ambient air, performance would suffer without additional cooling. The challenge was to get the requisite cooling air to the charge-air coolers without significantly widening the rear end of the car. An extensive redesign—albeit a barely noticeable one from the outside—was the result.
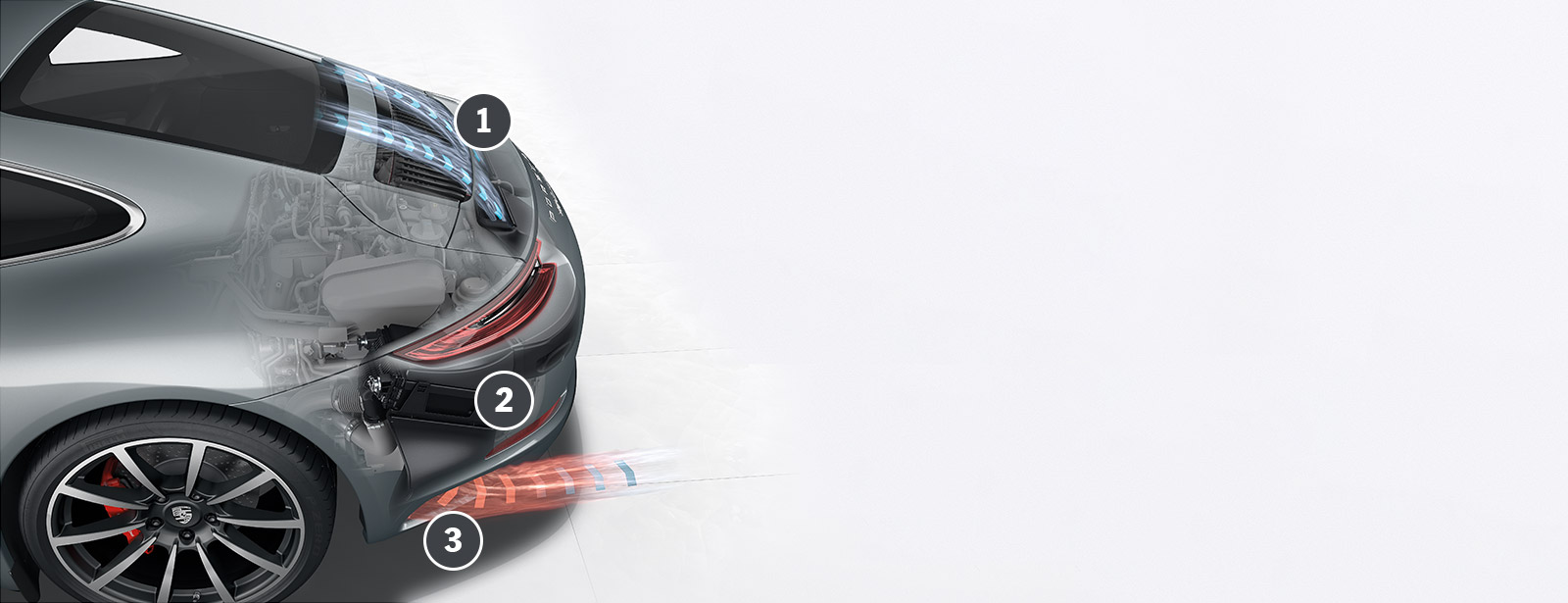

1 Collection
The outside air required to cool the charge air flows from the front of the rear spoiler.
2 Cooling
Two heat exchangers ensure significant cooling of the charge-air temperature.
3 Ventilation
The cooling air leaves the engine compartment through two outlets in the rear bumper. They are designed to generate a pressure difference.
As much as the turbocharging garners the attention, it is just one aspect of the new boxer engine generation. After all, when it comes to what’s new with these powertrains, the answer is practically everything. Take the direct fuel injection. For the first time, the fuel injectors are positioned centrally, that is, the injector is located directly between the four intake and exhaust valves. It propels the fuel into the cylinder at up to 250 bar, atomized into minuscule drops. This helps to distribute the fuel evenly in the combustion chamber, with smaller deposits on the walls, enabling better and cleaner combustion. The 911
In the mechanical part of the new engines, the objective was the lowest-possible weight and friction. The new crankcase unites both characteristics. The previous crankcase, made of a material with higher silicon content, was replaced with a low-alloy aluminum cast material. Thanks to the use of an innovative coating system, it is possible to do without heavy gray cast iron sleeves. Iron particles are applied to the mechanically roughened guide surfaces. The resulting surface is not only robust and resistant to fluctuating fuel qualities, but is also very low-friction. The entire cylinder crankcase weighs 1.5 kilograms less than before. Another 2 kilos are saved through the use of a composite oil pan and the omission of a secondary air system for emission control.
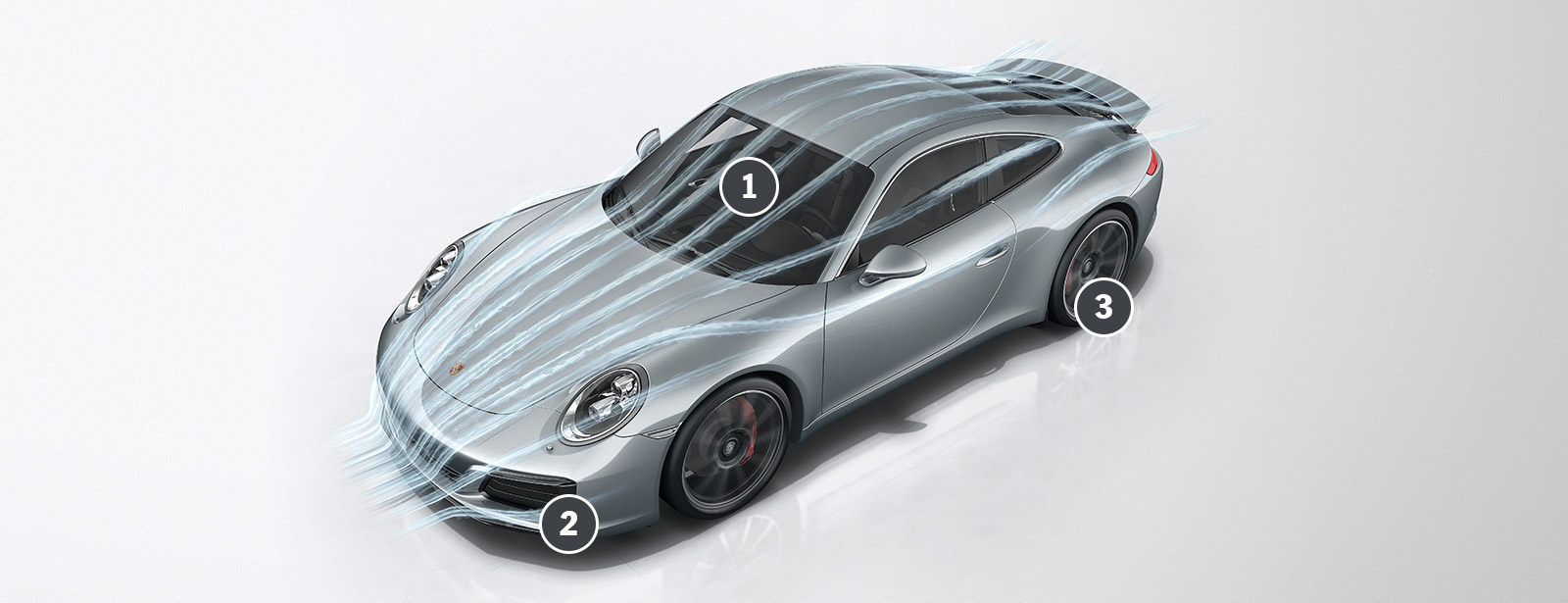

1 Optimal airflow
The new 911
2 Closed
At low engine loads, flaps in front of the radiator close to reduce drag.
3 Light
A new manufacturing method reduces the weight of the wheels, boosting both efficiency and comfort.
Lightweight construction is especially effective in reducing unsprung mass, for example at the wheels. The new 20-inch wheels don’t just look sleek and sprightly, but are also especially light thanks to a production process known as flow-forming. The process allows wall thicknesses that can otherwise only be achieved through forging processes—saving several hundred grams per wheel. On the rear axle, the wheels are half an inch wider—not least to put the imposing torque on the road safely. The rear wheels in the standard version are wider at 295/35 than was previously the case (285/35).
More muscular in appearance, agility has made gains as well, in particular when one adds the optional rear-axle steering. Opposite-direction steering simplifies parking by reducing the turning circle by up to 50 centimeters. At speeds over 80 km/h, the rear wheels steer in the same direction as the front wheels. The effect stabilizes the vehicle in fast corners or during rapid lane changes. Once again, one might conclude that we are witnessing the best 911 …
By Johannes Winterhagen